Why Gut Health is Crucial for Thyroid Function?
Many are unaware of how closely the gut and thyroid are linked. When gut health is compromised, it can directly affect thyroid function, leading to imbalances and exacerbating autoimmune conditions.
The Role of the Gut in Thyroid Health
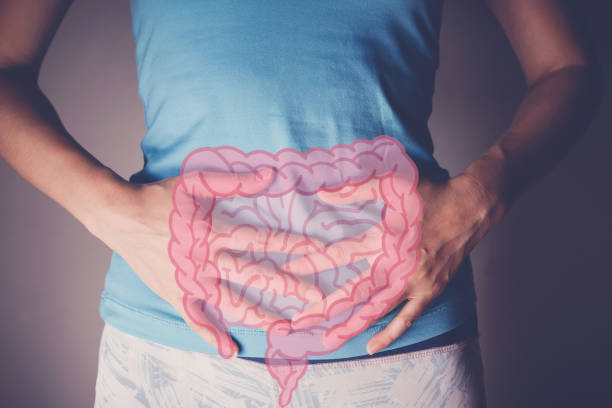
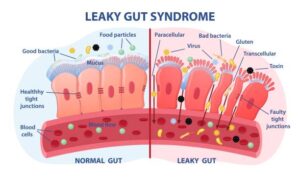
The gut is essential for digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune regulation. Its lining acts as a barrier, controlling nutrient absorption while blocking harmful substances like toxins and undigested particles. In those with autoimmune thyroid conditions, this barrier can become damaged, leading to “leaky gut” or intestinal permeability. When compromised, harmful substances enter the bloodstream, triggering an immune response and causing systemic inflammation, which can worsen thyroid dysfunction. Zonulin regulates the intestinal barrier, and its dysfunction disrupts immune balance. Restoring zonulin-dependent barrier function may help prevent or treat these diseases, as supported by clinical evidence.
Inflammation and Thyroid Dysfunction
When the gut becomes inflamed, it can lead to widespread inflammation throughout the body, including in the thyroid. This inflammation can exacerbate autoimmune responses and interfere with thyroid hormone production. As a result, people with Hashimoto’s or hypothyroidism may experience fatigue, weight gain, and difficulty managing thyroid hormone levels.
Leaky Gut and Thyroid Conditions
Even if someone with Hashimoto’s does not experience typical digestive symptoms, such as bloating, IBS, or gas, they may still have some degree of leaky gut. This emphasises the importance of focusing on gut health in the management of thyroid conditions, even when digestive symptoms are absent.
Healing the Gut to Support Thyroid Function
Improving gut health can significantly impact thyroid function. The first step in healing the gut is eliminating common irritants like gluten and processed foods, which can trigger inflammation and worsen autoimmune responses. Removing these from the diet can support gut healing. Additionally, incorporating anti-inflammatory foods such as vegetables, healthy fats, and clean proteins can reduce gut inflammation and support thyroid health.
Supporting the Gut Lining
Supporting the gut lining is essential for digestive health. Probiotics, digestive enzymes, and gut-healing foods help repair the gut barrier, improve nutrient absorption, and reduce inflammation. Many individuals with thyroid conditions, particularly Hashimoto’s, have deficiencies in hydrochloric acid (HCl) and digestive enzymes. These deficiencies hinder digestion and nutrient absorption, exacerbating fatigue and other symptoms. Without proper digestion, the body struggles to absorb the nutrients needed to support thyroid function, leading to further imbalances.
The Role of Stress in Gut and Thyroid Health
Stress management is also key. Chronic stress can impact both gut health and thyroid function. Stress hormones can increase gut permeability, exacerbate inflammation, and interfere with thyroid hormone regulation.
Conclusion: Prioritising Gut Health for Thyroid Health
By improving gut integrity, you can reduce inflammation, support thyroid function, and promote overall health. As a naturopath, I encourage my clients to prioritise gut health in managing thyroid dysfunction.
References
- Cardoso-Silva, D., Delbue, D., Itzlinger, A., Moerkens, R., Withoff, S., Branchi, F., & Schumann, M. (2019). Intestinal Barrier Function in Gluten-Related Disorders. Nutrients, 11(10), 2325. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102325
- Fasano, A. (2012). Leaky Gut and Autoimmune Diseases. Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology, 42(1), 71–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-011-8291-x
- Paray, B. A., Albeshr, M. F., Jan, A. T., & Rather, I. A. (2020). Leaky Gut and Autoimmunity: An Intricate Balance in Individuals Health and the Diseased State. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(24), 9770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249770